vaccine delivery system meaning
Administering a vaccine with unique and complex requirements made the development. This review will focus on recent developments in vaccine delivery systems.

Optimization Of Lipid Nanoparticles For Intramuscular Administration Of Mrna Vaccines Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
Drug delivery systems are engineered technologies for the targeted delivery andor controlled release of therapeutic agents.
. Examples of vaccine delivery systems include liposomes emulsions and. Vaccine delivery systems are generally particulate eg. Delivery of antigens from oil-based adjuvants such as Freunds 1 adjuvant lead to a reduction in the number of doses of vaccine to be administered but due to toxicity concerns like inductions of granulomas at the.
MNAs are minimally invasive. Immunisation involves the delivery of antigens to the mucosal immune system dispersed or organised into units such as Peyers patches in the intestine or the nasal-associated lymphoid tissue in the oropharangeal cavity. The COVID-19 pandemic and associated disruptions have strained health systems with 23 million children missing out on vaccination in 2020.
While immunization is one of the most successful public health interventions coverage has plateaued over the last decade. Adopting an intentional strategy to ensure equitable access to vaccine. 13 2020 photo provided by Los Angeles World Airports a FedEx Airbus A300F4-605R carrying the first batch of COVID-19 vaccine arriving in.
More than 32 million people in the state have contracted the virus and hospitals especially in Southern. Immunogenicity studies will be. Miniaturizing the vaccine delivery system also reduces the burden on the so-called cold chaina baton race from manufacturing plant to patient arm through a series of special refrigerated trucks and shipping containers designed to keep vaccines at sometimes arctic temperatures.
In this review we will introduce a few of the leading non-viral vaccines that are under clinical stage development and discuss delivery strategies to improve vaccine. It is ap- parent that the ability or willingness of a patient to pay for a vaccine may be less important than a providers interest in supplying it although both may be related to insurance status. Typically most vaccines are administered via the subcutaneous SC or intramuscular IM routes.
Patches are typically kept on for 1-2 days. Each vaccine exhibits a different potency and duration of efficacy as determined by the antigen design adjuvant molecules vaccine delivery platforms and immunization method. All reported numbers may change over time as updated data are continuously reported to CDC.
A COVID-19 Vaccine Delivery Method Guide. As governments across the world commence the procurement of a vaccine there is an urgent need to elevate resilience of existing systems and their ability to effectively manage the scale and speed of successfully delivering the vaccine doses. Drugs have long been used to improve health and extend lives.
Timely and accurate reporting from jurisdictions drives the information reported by CDC. We will discuss each of these briefly in the following slides. Health care personnel should always perform hand hygiene before administering vaccines by any route.
The common routes of vaccine delivery are parenteral injection needle-free injections intranasal ocular oral and spray topical. Hypodermic injections are associated with pain and distress that might lead to poor patient compliance and require highly trained personnel for administration. The antigen delivery systems may comprise a simple buffer solution withwithout adjuvants or an advanced particulate formulation such as liposomes or.
CDC reports COVID-19 vaccination data online on COVID Data Tracker and in vaccination datasets. Global Novel Vaccine Delivery System Market is valued at approximately USD Billion in 2020 and is anticipated to grow with a healthy growth rate of more than over the forecast period 2022-2030. Advanced immunoimaging resources in our Stem Cell Research Center will be used to determine bioavailability and track delivery of vaccine into the draining lymph node.
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease. Each vaccine has a recommended administration route and site. It doesnt have as much meaning as creating something.
In this late Sunday Dec. The preprint described Modernas coronavirus vaccine candidate as using delivery technology that appears to be covered in the Arbutus patent that was upheld last week. Delivery of DNA by live vectors is quite efficient relative to naked DNA vaccines.
What are drug delivery systems. This information is included in the manufacturers package insert for each vaccine. This review will focus on recent developments in vaccine delivery systems.
Appropriate vaccine administrationdelivery is the key element to ensure successful vaccination. DELIVERY SYSTEMS 105 termining eligibility high costs of stocking vaccine inventories and low payment rates for administering vaccines as discussed above. Deviation from the recommended route may reduce vaccine efficacy or increase local adverse reactions.
MNAs can be easily self-administered without professional training. Product Delivery Research. MNAs are tiny patches of micro-needles about the thickness of a fingernail that can deliver vaccines and other medicines.
Grounding Principles King Countys pledge to equitable vaccine delivery is rooted in a deep commitment to equity and social justice. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease-causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe its toxins or one of its surface proteinsThe agent stimulates the bodys immune system to recognize the agent. Newsom on Monday said the state has tripled its rate of administration of the vaccine.
The preprint of the study. Emulsions microparticles iscoms and liposomes and mainly function to target associated antigens into antigen presenting cells APC including macrophages and dendritic cells. Vaccine formulations will be developed and characterized in the Pharmaceutical Sciences Biomedical Engineering and Chemistry Departments.
Vaccine delivery systems are generally particulate eg. Vaccinations in the United States. A vaccine delivery system is the means by which the immune-stimulating agent constituting the vaccine is packaged and administered into the human body to ensure that the vaccine reaches the desired tissue.
Innovative Vaccine Delivery Technologies Approaches. And aligned with PHSKC and the King County Executives declaration that racism is a public health crisis. The practice of drug delivery has changed dramatically in the past few decades and even greater changes are anticipated in the.
Various gene delivery systems include intracellular bacteria such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis Listeria monocytogenes Salmonella typhi and Shigella flexneri viruses such as vaccinia adenovirus and avipox and plasmid DNA. Emulsions microparticles iscoms and liposomes and mainly function to target associated antigens into antigen presenting cells APC including macrophages and dendritic cells. This photo shows a r esponder at an.

Vaccines How To Develop A Vaccine
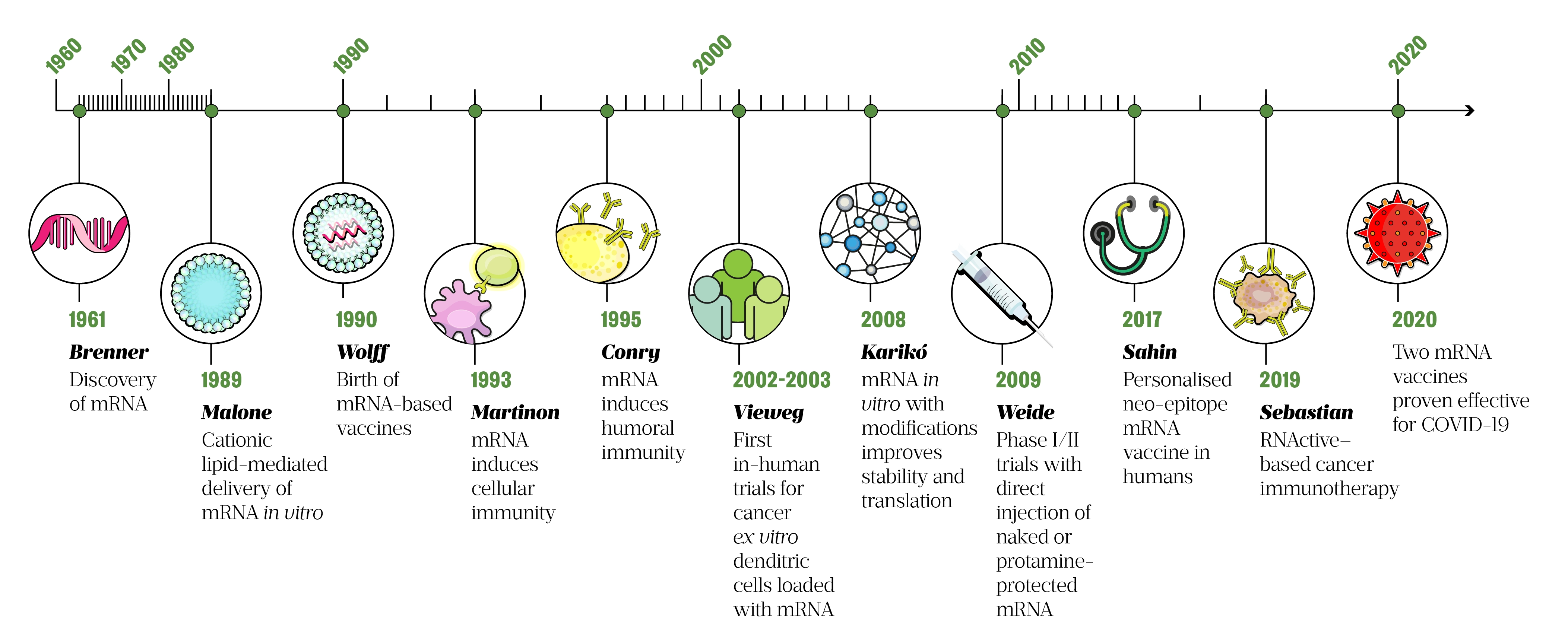
Understanding Mrna Vaccine Technologies The Pharmaceutical Journal

Essential Programme On Immunization

How Vaccines Work British Society For Immunology

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine
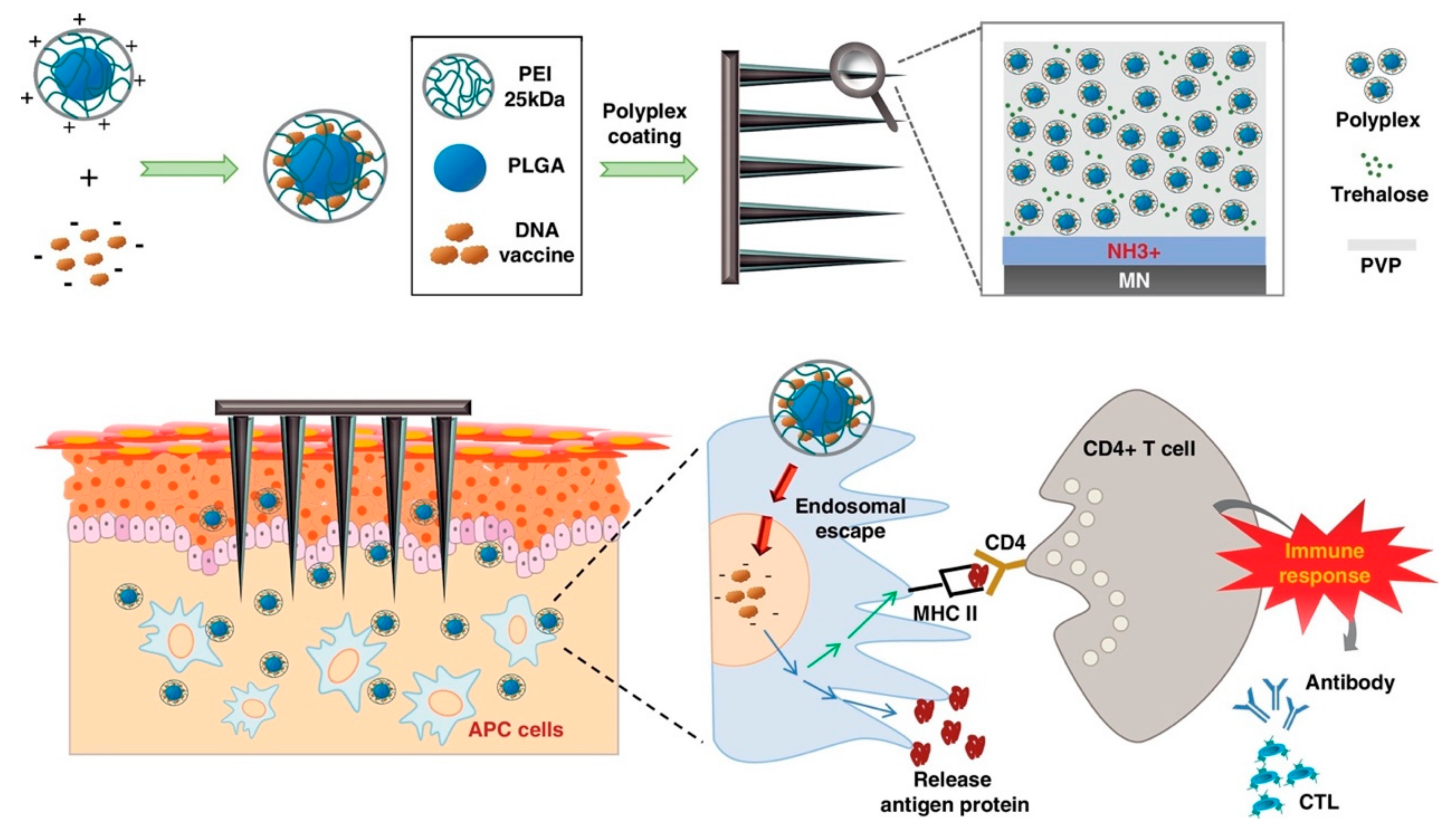
Pharmaceutics Free Full Text Engineered Nanodelivery Systems To Improve Dna Vaccine Technologies Html

Virosome An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

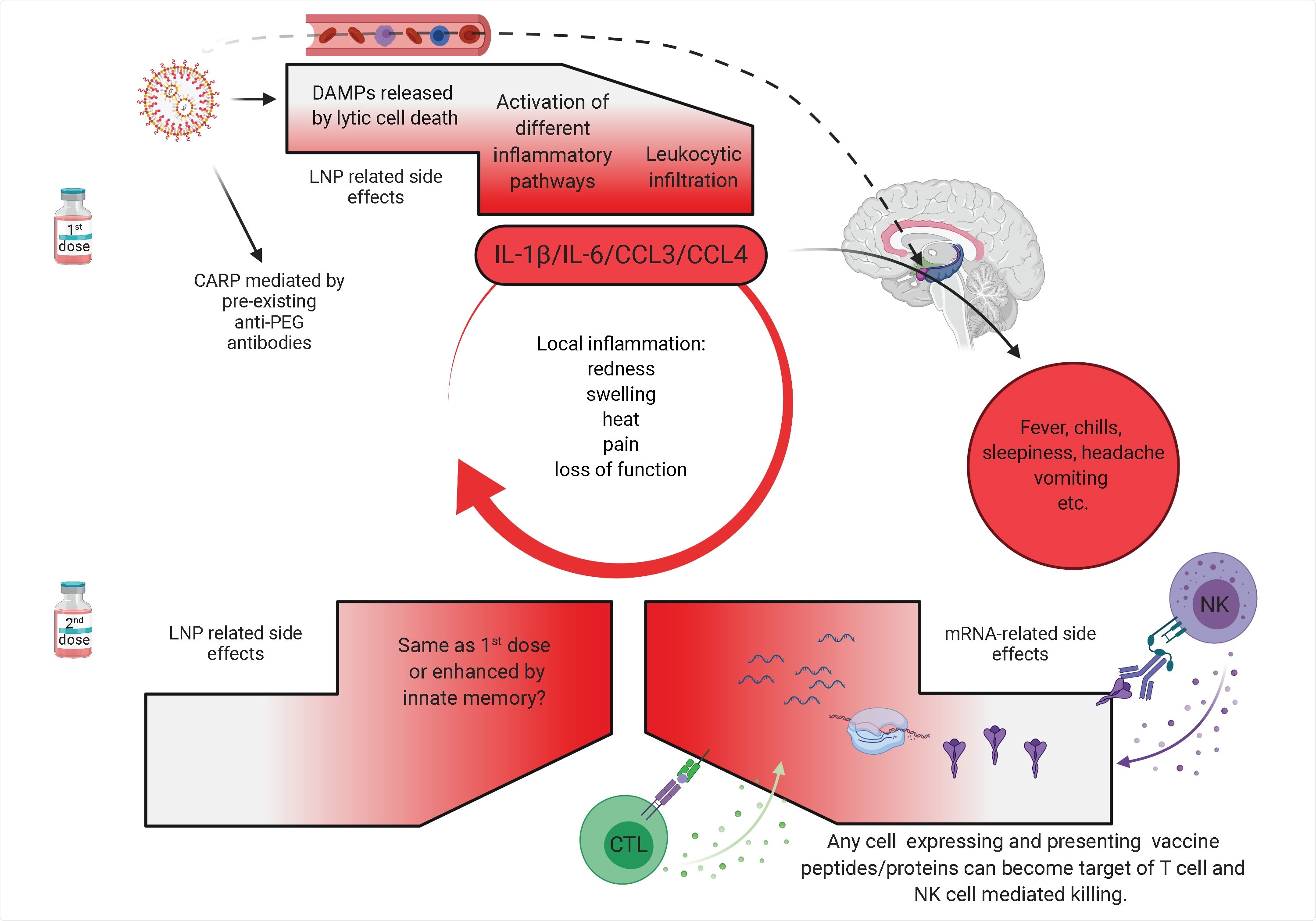
Research Looks At Inflammatory Nature Of Lipid Nanoparticle Component In Mrna Vaccines
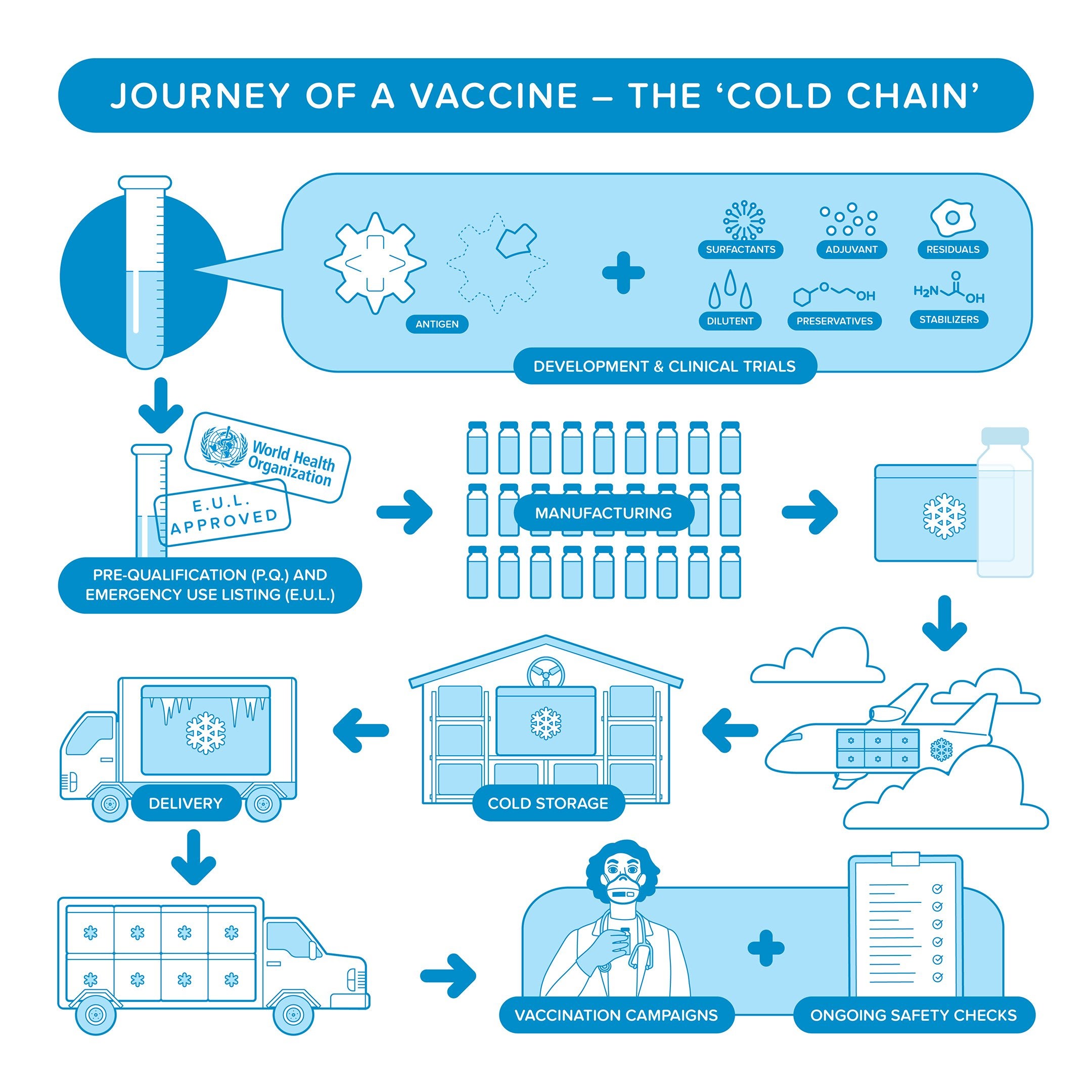
Cold Chain Paho Who Pan American Health Organization
Perceived Enablers And Barriers Of Community Engagement For Vaccination In India Using Socioecological Analysis Plos One
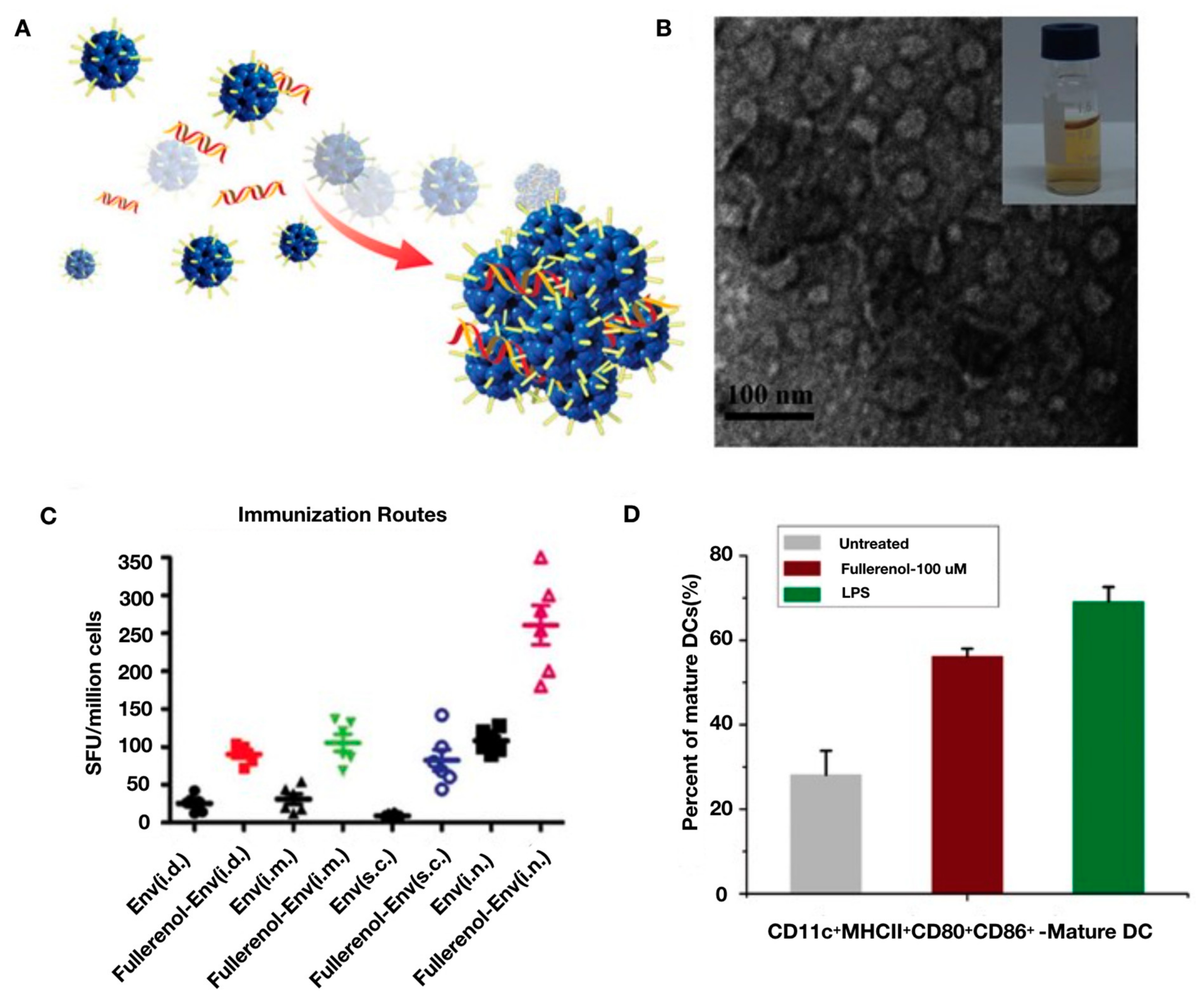
Pharmaceutics Free Full Text Engineered Nanodelivery Systems To Improve Dna Vaccine Technologies Html
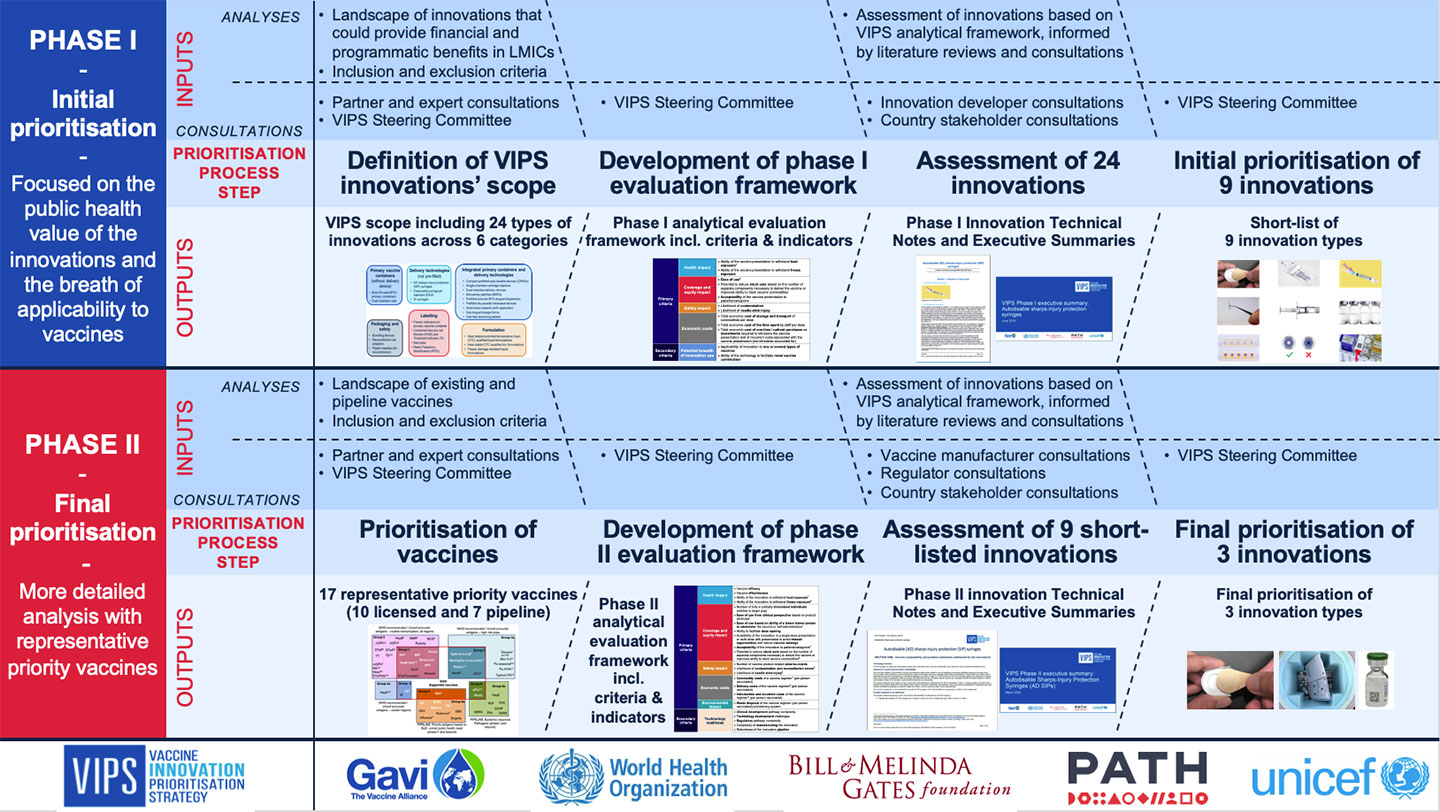
The Vaccine Innovation Prioritisation Strategy

Mucosal Vaccination British Society For Immunology
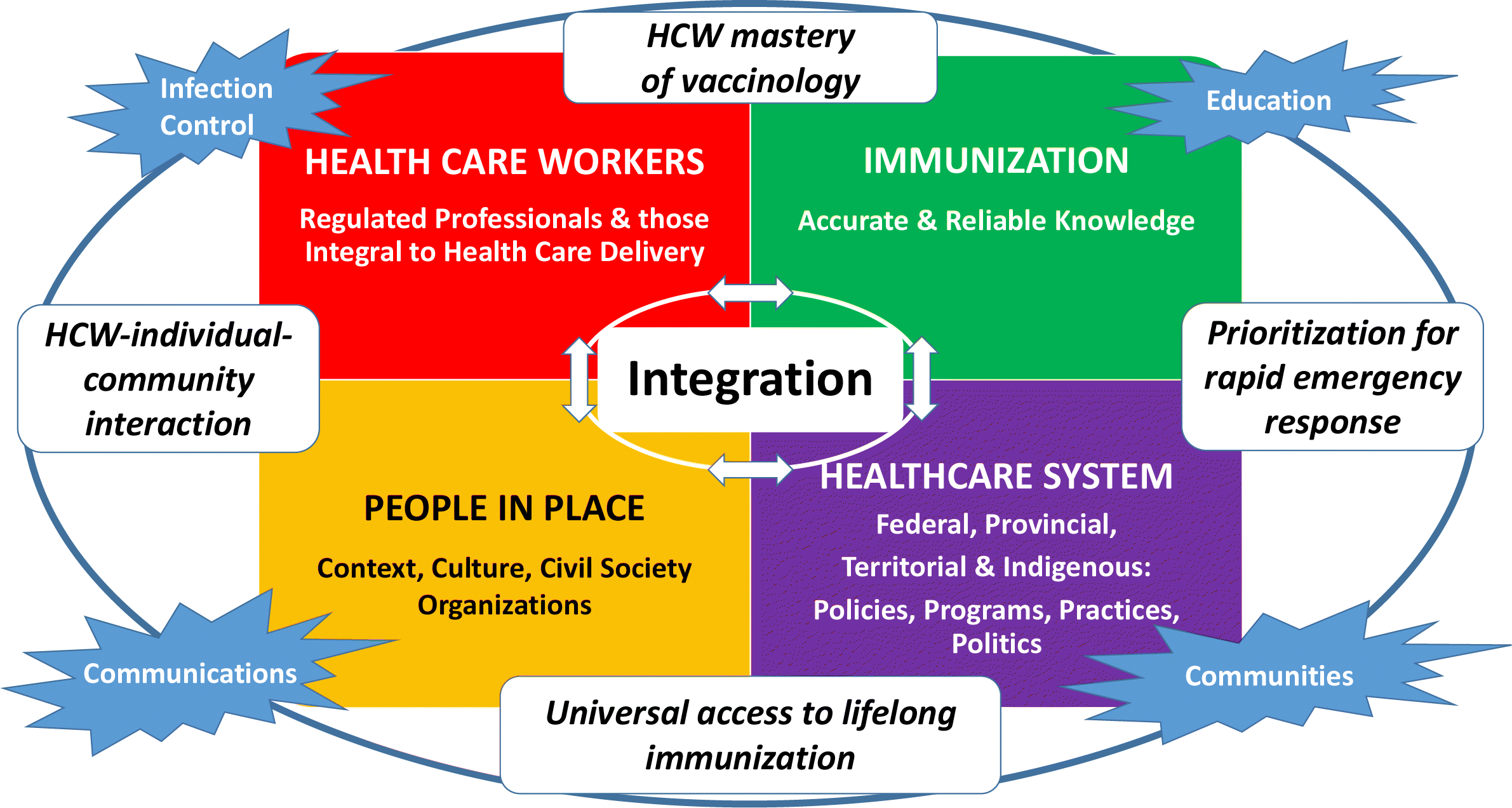
Royal Society Of Canada Covid 19 Report Enhancing Covid 19 Vaccine Acceptance In Canada

Intranasal Covid 19 Vaccines From Bench To Bed Ebiomedicine

Efficacy Of A Low Dose Candidate Malaria Vaccine R21 In Adjuvant Matrix M With Seasonal Administration To Children In Burkina Faso A Randomised Controlled Trial The Lancet
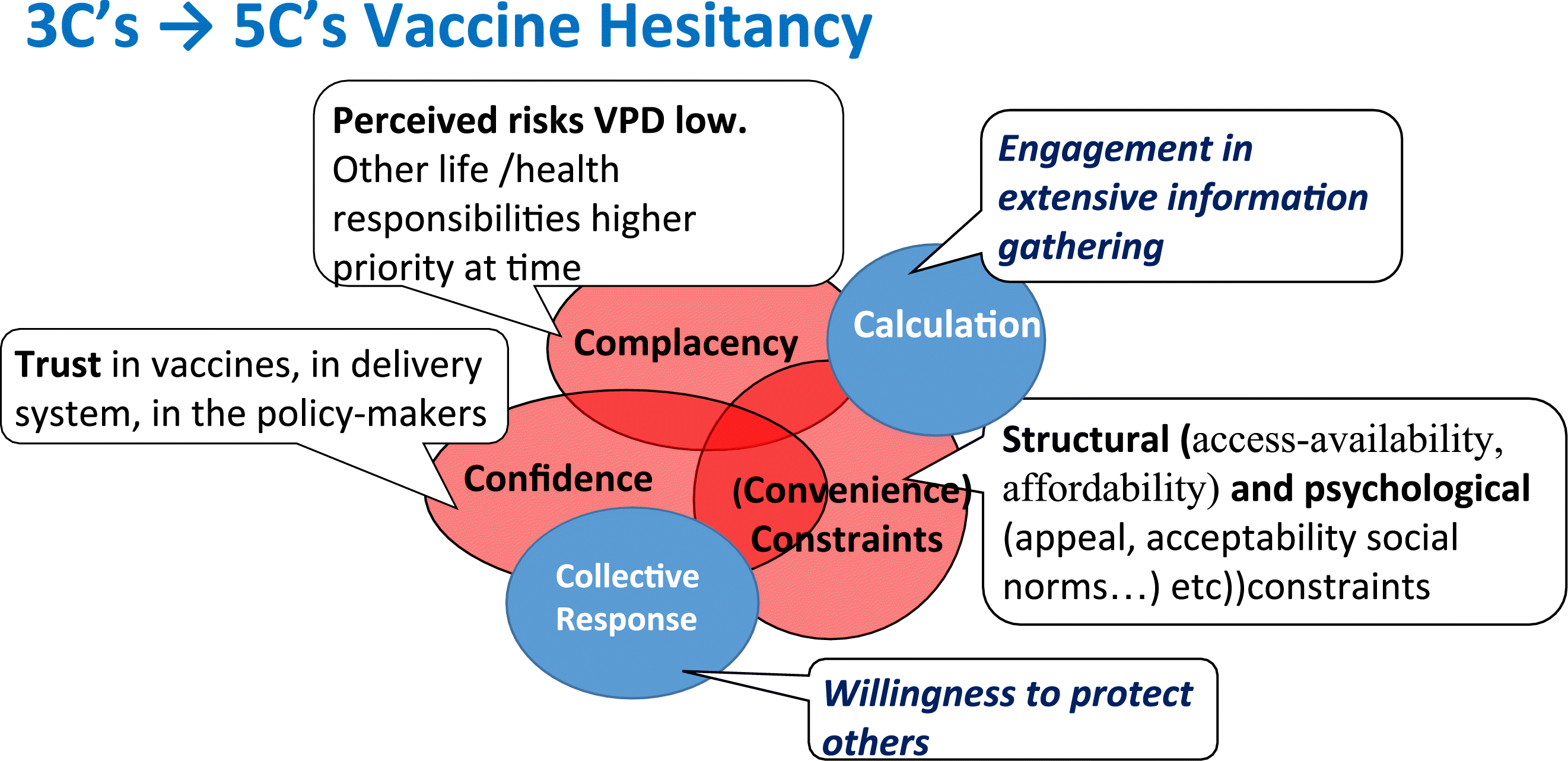
Royal Society Of Canada Covid 19 Report Enhancing Covid 19 Vaccine Acceptance In Canada

Covid 19 Vaccines For Homebound Patients And Their Caregivers Catalyst Non Issue Content
Understanding Mrna Vaccine Technologies The Pharmaceutical Journal